SCE Risk & Reliabiity

- CONTACT US
-
Our Address
FZC RAK Free Trade Zone ,
PO Box : 40046 ,
RAK Ras Al Khaimah – UAE.
Tel : +971 720 76161,
Mobile : +971 50 772 0031,
+971 50 582 1953
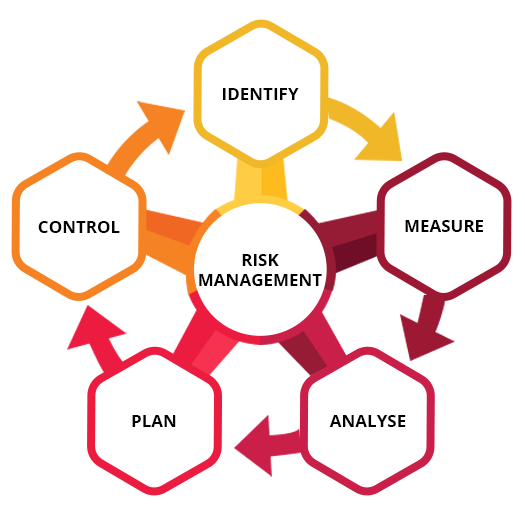
The need for safe operation of industrial facilities, such as nuclear power plants, chemical and petroleum processes and manufacturing facilities that use hazardous materials and operation, has led to the development of analytical methods for risk and reliability assessment. These methods employing probabilistic calculations, quantify the various sources of uncertainty and randomness in system components and hence find increasing applicability in various engineering systems and related industries for hazard evaluation and reliability and availability enhancement. Industries and regulatory bodies for various engineering sectors such as Transport, Medial, Manufacturing, Automobile, etc, recommend probabilistic analysis for evaluating the effectiveness of their design with respect to risk and availability.
By employing proven methods, our team is capable of providing consultancy services for increasing the system and component safety and reliability for various engineering applications.
RBDs help assess reliability and availability of systems and components by modeling the system components into series and parallel arrangements based on the components redundancy or logical configuration. RBDs are used to further evaluate the availability, reliability of failure probability of the system.
FMECA (Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis) analyzes potential failure within a system, identifies the potential causes and effects/hazards associated with these failures, and classifies them according to their severity. It is then possible to assess the risk associated with the identified failure modes, effects and causes, and prioritize corrective actions.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a powerful analytical technique, which is applied for system analysis for assessing failures, to calculate unreliability and unavailability, to analyze Common Cause Failure (CCF) etc. For FTA modeling an undesired state of a system (called top event) is specified, usually a state that is critical from a safety or reliability standpoint. The system is then analyzed in the context of its environment and operation, to find all realistic ways in which the top event can occur. FTA is a graphic model of various parallel and series combinations of faults that will result in the occurrence of the top event. Faults can be events that are associated with component or equipment failures, human errors, software errors, or any other pertinent events, which can lead to the top event.
The Event Tree analysis is a flexible tool that helps in analyses of event probabilities and multiple consequences. ETA Model uses logic diagrams to determine the path from an initiating event to the various consequences, and the expected frequency of each consequence. Cut set and other important analysis results can be displayed and reported in several different ways. Event trees. The failure probability of these defence-in-depth levels can be obtained using historical failure data or logical models as FTA or RBD. Initiating events can be internal or external events, which can create extreme environments to several plant systems.
Sneak Circuit Analysis is a vital part of the safety assurance of safety-critical electronic and electro-mechanical systems.
Sneak conditions are defined as latent hardware, software, or integrated conditions that may cause unwanted actions or may inhibit a desired function, and are not caused by component failure.
Sneak Circuit Analysis (SCA) is used in safety-critical systems to identify sneak (or hidden) paths in electronic circuits and electro-mechanical systems that may cause unwanted action or inhibit desired functions. The analysis is aimed at uncovering design flaws that allow for sneak conditions to develop. The sneak circuit analysis technique differs from other system analysis techniques in that it is based on identification of designed-in inadvertent modes of operation and is not based on failed equipment or software.
PO Box : 40046 RAK, UAE
PO Box: 682020 Kochi, India
PO Box 570008, Centre for I&S, NIE, Mysuru
Please fill in all details to serve you better